Comparing Veneer, Laminate, and Thermofoil Finishes for Cabinets
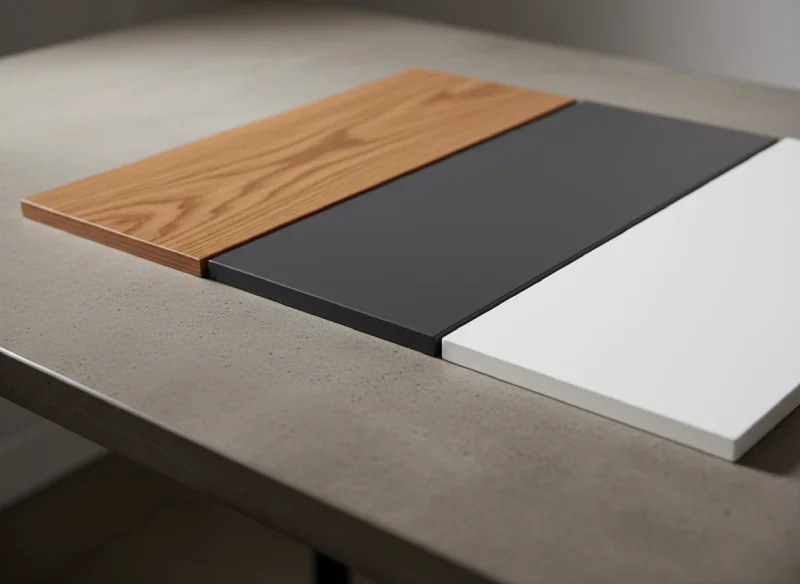

Veneer offers real wood beauty, laminate brings scratch-resistant durability, and thermofoil gives budget-friendly consistency — the best choice depends on your priorities for style, cost, and wear.
Choosing between veneer, laminate, and thermofoil for your cabinets or furniture isn’t just a design decision — it affects durability, maintenance, cost, and long-term value, which is why a design build home contractor often helps homeowners evaluate the best option for their space.
Each finish has its advantages: veneer offers the warmth of real wood, laminate resists daily abuse, and thermofoil provides a seamless, affordable surface. In this guide, we break down the pros and cons so you can choose the best finish for your project.
Key Takeaways
- Veneer gives real wood grain and can be refinished, but it's more delicate and expensive.
- Laminate is scratch-resistant, stain-proof, and affordable — ideal for heavy-use areas.
- Thermofoil offers a seamless, low-cost surface but is prone to heat and moisture damage.
- Each finish differs in repairability, appearance, and environmental impact.
- Choose based on budget, usage, and design goals — request samples and compare warranties before buying.
What Is Wood Veneer and When to Use It
Definition and Benefits
Wood veneer is a thin slice of real wood applied by a custom cabinet maker to a stable backing like MDF or plywood. It delivers an authentic wood look without the cost or expansion issues of solid wood.
Best Uses
- Cabinet doors and drawer fronts
- Furniture panels
- Accent walls or millwork
Pros
✅ Natural wood appearance
✅ Can be refinished or stained
✅ Lighter and more stable than solid wood
Cons
❌ Higher cost
❌ Susceptible to moisture if not sealed
❌ Needs gentle cleaning
Laminate Finishes: Durable and Budget-Friendly
Types of Laminate
- HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) – Strong, heat- and scratch-resistant
- LPL (Low-Pressure Laminate) – More affordable, commonly used by cabinet makers in mass-produced cabinetry
Ideal Applications
- Kitchen countertops
- Office furniture
- Cabinet exteriors and shelving
Pros
✅ Highly durable and affordable
✅ Easy to clean
✅ Wide design selection
Cons
❌ Hard to repair if chipped
❌ Edges may peel without quality banding
Tip: Use laminate in high-traffic spaces like kitchens, kids’ rooms, and rental properties.
Thermofoil: Seamless and Cost-Efficient
What Is Thermofoil?
Thermofoil is a thin vinyl layer heat-bonded to MDF, giving a smooth, painted-like finish that resists stains and is easy to clean.
Where It Works Best
- Budget kitchen or bathroom cabinets
- Laundry rooms or rental units
Pros
✅ Seamless, low-maintenance surface
✅ Uniform color and texture
✅ Affordable with easy cabinet installation
Cons
❌ Prone to peeling near heat sources
❌ Difficult to repair
❌ Lower lifespan in humid or hot areas
Durability, Maintenance, and Repair Comparison
| Feature | Veneer | Laminate | Thermofoil |
| Scratch Resistance | Moderate | Excellent | Good |
| Heat Resistance | Good | Good | Poor |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate (if sealed) | High | Low |
| Repairability | Refinishable | Hard to repair | Replace if damaged |
| Cleaning | Gentle cleaners only | Easy with soap/water | Easy, but no steam cleaners |
Cost and Environmental Factors
| Finish | Avg. Cost | Eco Notes |
| Veneer | $$$ | Renewable wood, lower waste than solid wood |
| Laminate | $–$$ | Some contain formaldehyde, but durable |
| Thermofoil | $–$$ | PVC-based, VOC potential, less recyclable |
For more on materials and indoor air quality, visit EPA guidelines on VOCs.
How to Choose the Right Finish for Your Project
Step-by-Step Breakdown:
- Set Priorities – Aesthetic, durability, budget, maintenance
- Compare Surfaces – Use samples for texture and color
- Match to Use Case
- Veneer: high-end looks
- Laminate: heavy-use areas
- Thermofoil: low-cost, uniform styles
- Check for Warranty and Moisture/Heat Tolerance
- Evaluate Long-Term Repair Costs and professional cabinet installation needs
Conclusion
When choosing between veneer, laminate, and thermofoil, the best option depends on your goals for appearance, durability, and budget. Veneer delivers a premium real-wood look. Laminate offers unmatched toughness and style flexibility. Thermofoil provides seamless, affordable ease — but with some tradeoffs in heat resistance and longevity.
Need help picking the right finish? Talk to a custom cabinet maker at CabStone installer. We'll match your vision with the right material for long-term performance and beauty.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the most durable finish for high-use cabinets?
Laminate is the most durable and scratch-resistant for daily wear.
Can I repaint or refinish thermofoil cabinets?
Not effectively — once damaged, thermofoil often needs full panel replacement.
Is veneer better than laminate?
Veneer offers a real wood appearance and can be refinished, but laminate is tougher and lower-maintenance.
How long does thermofoil last?
Around 5–10 years with light use; less in high-heat or high-humidity environments.
Are these finishes safe for indoor air quality?
Veneer and some laminates are low-VOC; thermofoil may release VOCs depending on adhesives — always ask for certification (e.g., CARB-compliant).
Can I mix finishes in the same space?
Yes — for example, use thermofoil doors with laminate boxes or veneer accents.
What finish looks most like painted wood?
Thermofoil gives the most consistent, paint-like finish, though some high-gloss laminates also achieve this look.
Which finish is best for rental properties or commercial spaces?
Laminate is ideal for rentals and commercial settings due to its durability, stain resistance, and low maintenance needs.
Can veneer cabinets be used in bathrooms?
Yes, but only if they are properly sealed and the bathroom is well-ventilated. Moisture can damage unsealed veneer over time.
What is the difference between HPL and LPL laminate?
HPL (High-Pressure Laminate) is more durable and heat-resistant, while LPL (Low-Pressure Laminate) is more affordable but better suited for lighter-use applications.